What is Spondylitis?
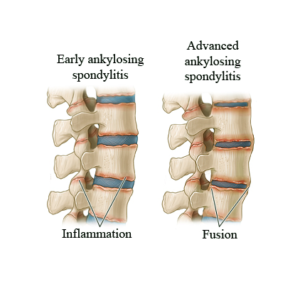
Spondylitis is a condition that causes inflammation in the spine, specifically in the vertebrae and the spinal joints (also known as facet joints). If the condition is severe, the facet joints and vertebrae can swell and move out of alignment in the spine. This can restrict movement, cause stiffness and possibly impact a surrounding nerve.
If you notice the development of these symptoms, and you are not able to find relief after a week of resting, taking anti-inflammatory medication and applying hot/cold compresses, you should schedule an appointment with your doctor. Your physician can review your symptoms and order an MRI to determine if spondylitis is the cause of your pain. Once you are diagnosed, you and your doctor can have a conversation about what type of spondylitis you have, what caused your condition and the treatment options available to you.
Causes of spondylitis
Spondylitis is a complex spine condition. The exact cause is unknown, but research strongly suggests that genetics play a main role in the development of the disease. This is evidenced by the fact that the majority of people with spondylitis carry a gene called HLA-B27. This gene is found in more than 95 percent of Caucasian people with ankylosing spondylitis, although in other ethnic groups, the association between the presence of HLA-B27 and the development of ankylosing spondylitis varies. In addition, the majority of people with HLA-B27 never develop ankylosing spondylitis, so it’s clear that something else is involved in starting the disease. Some additional risk factors for developing spondylitis include:
- Bacterial infections. Bacterial infections, particularly those in the gastrointestinal tract, appear to trigger ankylosing spondylitis in people who have the genetic makeup for the disease.
- Having family members with ankylosing spondylitis. People with the HLA-B27 gene who have relatives with ankylosing spondylitis are more likely to develop it themselves.
- The presence of other genetic markers. Other genes, including IL23R and ARTS1, appear to be linked to the development of ankylosing spondylitis.
Spondylitis Symptoms
Symptoms of spondylitis vary depending on the individual and the location and severity of the condition. The common symptoms of spondylitis include:
- Stiffness and pain in the neck or back
- Loss of mobility in the spine
- Inability to twist and turn or to do so without pain
- Chronic pain and discomfort when standing, sitting or walking
- Deformity or an abnormal spine curvature
If you are experiencing these symptoms, you should consult your doctor to seek treatment options available to you.
Treatment options for spondylitis
Your doctor will likely begin your treatment with conservative pain relief options, such as physical therapy, hot/cold compresses, stretches and pain medication. Many conservative treatment options are available to you, so you and your doctor can work together to find the combination of therapies that best relieves your pain.
If you do not respond to conservative treatment, you may need to consider a surgical option.